IVF is a process of fertilization where an egg is combined with sperm outside the body, in vitro (“in glass tube”). The process involves monitoring and stimulating woman’s ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from the woman’s ovaries and letting sperm fertilize them in a liquid in the laboratory.

IVF is the process of fertilization by extracting eggs, retrieving a sperm sample, and then manually combining an egg and sperm in a laboratory dish using ICSI.
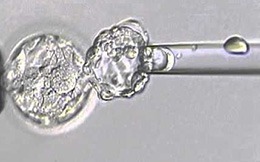
Single sperm may be injected directly into the egg using intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
After ICSI it will be left in the medium for 24 hours.
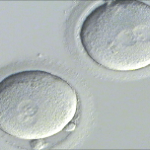 The next day, the eggs are examined under a microscope to determine whether fertilization has occurred and you will be phoned about how many of your eggs have been fertilized.
The next day, the eggs are examined under a microscope to determine whether fertilization has occurred and you will be phoned about how many of your eggs have been fertilized.
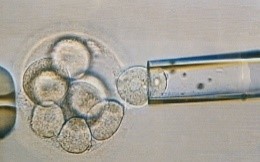
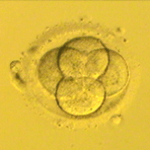 Two days after fertilization, normal embryos are between two and six cells.
Two days after fertilization, normal embryos are between two and six cells.
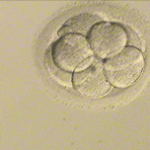 Three days after fertilization, most normal embryos are between seven and nine cells.
Three days after fertilization, most normal embryos are between seven and nine cells.
 Four days after fertilization, most normal embryos have reached the morula stage (too many cells to reliably count with a microscope).
Four days after fertilization, most normal embryos have reached the morula stage (too many cells to reliably count with a microscope).
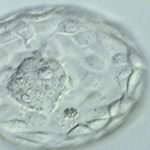 Embryos will be observed until it will be transferred to the IVF patient.
Embryos will be observed until it will be transferred to the IVF patient.
aCGH is a method applied prior to transfer of the embryos into the uterus during in vitro fertilization (IVF) process which allows the embryos to be examined not for only certain chromosomes selected by FISH method but all the chromosomes present (24 different chromosomes). The assay is performed by using a technique called Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (named “aCGH” in short), using micro-chip technology containing thousands of particles from human chromosomes. Since the entire chromosomal map of embryos examined can be seen with this method, many abnormalities at chromosome level that couldn’t be detected can now be detected. Also; we analyse 20000 gene mutations and over 1000 genetic diseases.
The Comprehensive Chromosome Screening
Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) method, which had been used for a long time to increase the success of pregnancy for couples who want to have a baby but failed or had a miscarriage, has now been replaced by longer Comprehensive Chromosome Screening approach. This new approach, recognized as a promising new hope for IVF, is successfully performed at Faruk Medical City (FMC) IVF centre.
Although your doctor will try to fertilize all available eggs, usually only one, or occasionally two, embryos will be transferred immediately. If there are any remaining embryos, they can be frozen through a process known as cryopreservation. Frozen embryos are stored and most will remain unchanged for a long period of time. The majority of embryos will survive the process of freezing and thawing. For an advantage of cryopreservation is that these frozen embryos can be used in future IVF/ assisted reproductive technologies ART cycles without having to repeat the first few steps of ovarian stimulation, egg recovery and fertilization.
We can keep your frozen Egg, Sperm or Embryo for 4 years.
- Ovulation disorders
- Blocked fallopian tubes or missing tube
- Endometriosis or Myomas
- Severe pelvic adhesions
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
- Cervical problems
- Low Ovarian Reserve
- Azospermia or No Sperm
- Insufficient sperm morphology
- Sperm motility (slow moving sperm)
- Low sperm count
- Blockage of sperm release such as Vasectomy
Surgical sperm extraction when a man does not have any sperm in his ejaculated semen because of blockage, failed sterilization reversal, or other reasons, sperm can be surgically extracted from the epididymis or testicular tissue, where they are stored.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) is usually recommended for pairs that are deficient or not fertilized during the standard IVF, but are often used to come from above the male infertility. It was used for the first time in 1992 and offers an alternative to donor sperm for those with severe male infertility.

